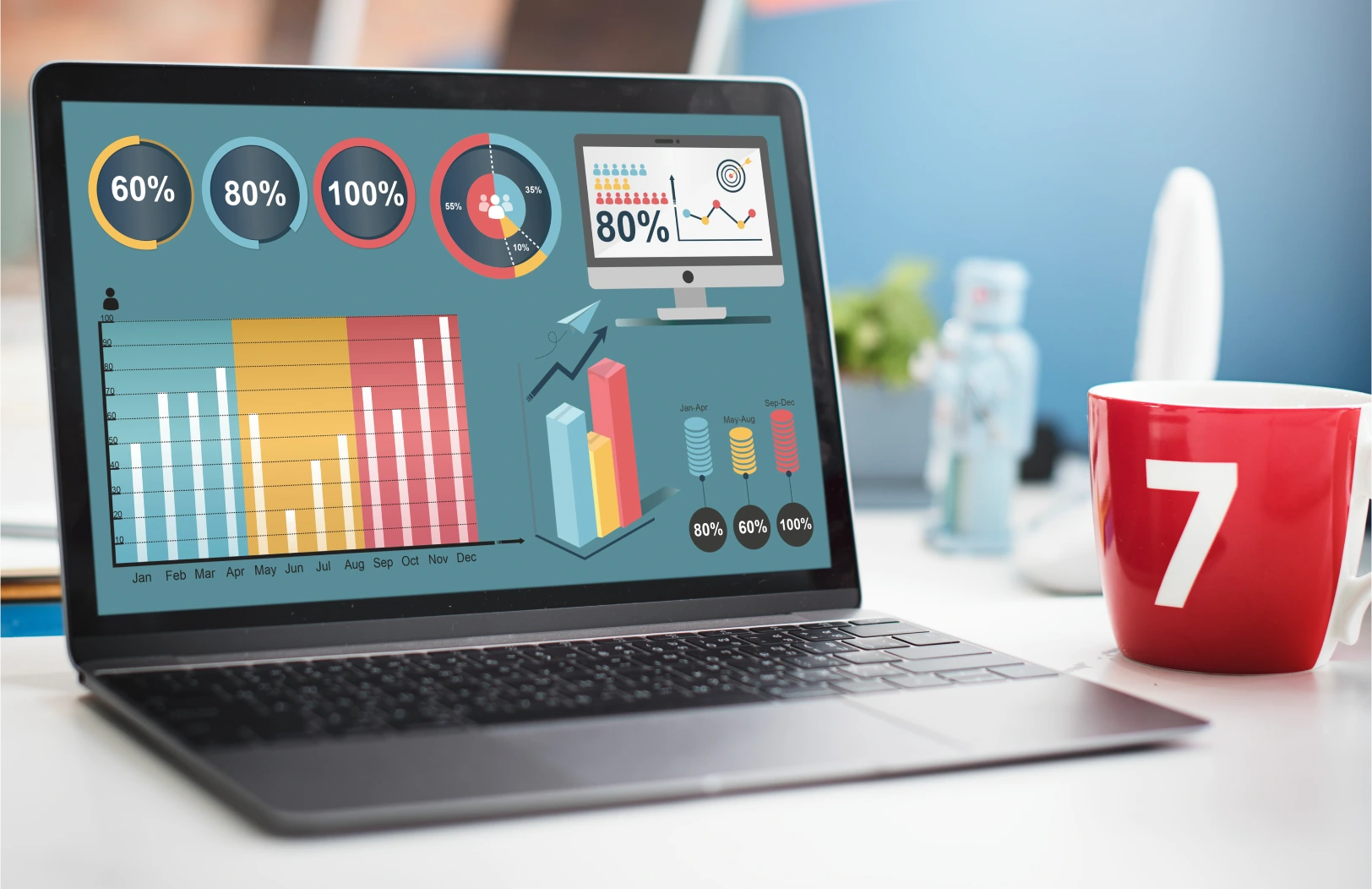
Website traffic, particularly when analyzed through GA4, is more complex than it may appear. For website owners, understanding this complexity is critically important. Among all types of traffic, one category tends to raise the most questions: direct traffic.
What is direct traffic? Where does it originate? How does it differ from other sources such as organic, referral, or unassigned traffic?
Most importantly, how can you apply direct traffic strategies to ensure cleaner data, more reliable reporting, and better decision-making?
This guide explores these questions in depth, offering practical insights and expert recommendations to help you manage and interpret your website’s traffic data more effectively.
Understanding Traffic Sources in Google Analytics
In Google Analytics, website traffic is grouped into several key channels, each representing how visitors arrive at your site:
- Direct Traffic: Users who access your site by typing the URL directly into their browser or using bookmarks. This category may also capture visits where the referral source is missing or incorrectly attributed.
- Organic Traffic: Visitors who discover your website through unpaid search engine results.
- Referral Traffic: Sessions that originate from links on external websites directing users to your site.
- Social Traffic: Traffic driven from social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, and others. These sessions can come from both organic posts and paid campaigns.
- Unassigned Traffic: Visits that don’t align with predefined categories, often caused by tracking gaps or configuration issues.
Recognizing and differentiating these channels is vital for accurate reporting and for shaping effective digital marketing strategies.
Social Traffic and Its Impact on Attribution
Social traffic is frequently undervalued, as marketers often prioritize organic and direct channels. However, social platforms are a powerful driver of both engagement and conversions.
With the use of UTM parameters, traffic from social media becomes easier to track and analyze in Google Analytics. This applies not only to unpaid posts, but also to boosted content and paid social advertising campaigns.
Without consistent tagging, some social visits may be misclassified as direct traffic, particularly from mobile apps like Instagram or Facebook Messenger, which often remove referrer data.
To ensure accurate attribution, marketers should routinely review their social traffic sources and apply consistent tagging methods as part of a broader direct traffic management strategy.
Why Direct Traffic Is More Complicated Than It Seems
Several factors can contribute to inflated direct traffic numbers in Google Analytics:
- Missing or Improper Tracking Codes: If pages lack the correct Google Analytics tracking implementation, referral data may not be captured, causing visits to default to direct traffic.
- HTTPS to HTTP Transitions: When users move from a secure (HTTPS) site to a non-secure (HTTP) site, referral data is stripped, and the session is logged as direct traffic.
- Untracked Social Shares and Dark Social: Links shared via private channels such as email, messaging apps, or SMS often lack referral data, which results in direct traffic classification.
- Links in Non-Web Documents: Clicks originating from documents like PDFs, Word files, or presentations don’t pass referral information, leading to misattribution as direct traffic.
Resolving these challenges is essential to building effective direct traffic solutions and maintaining accurate analytics data.
Proven Methods for Precise Traffic Attribution
Ensuring precise traffic attribution is essential for understanding how users reach your website and for making informed marketing decisions. Implementing effective strategies helps prevent misattribution and provides a clearer picture of your traffic sources.
- Use Consistent UTM Tagging: Apply standardized UTM parameters across all marketing campaigns to accurately track traffic sources.
- Verify Tracking Code Deployment: Regularly audit your website to ensure every page has the correct Google Analytics tracking code installed.
- Maintain Redirects and Protocol Consistency: Ensure that redirects preserve referral data and that your website consistently uses HTTPS to protect source information.
- Review Referral Exclusion Lists: Regularly update your referral exclusion list to prevent legitimate traffic from being misclassified as direct.
- Educate Content Creators: Encourage the use of properly tagged links in all downloadable content and shared documents to capture referral data effectively.
By implementing these strategies, you can achieve more accurate traffic data, providing a solid foundation for informed marketing decisions and optimized campaign performance.
Common Pitfalls in Traffic Attribution
Even seasoned marketers can encounter challenges when interpreting traffic sources. Some of the most frequent mistakes include:
- Relying Only on Default Google Analytics Reports: GA’s standard traffic categorization isn’t always precise. Using custom reports and additional tracking layers can provide deeper insights.
- Overlooking Dark Social Traffic: Untracked link sharing via direct messages, emails, and internal chats can inflate direct traffic numbers.
- Neglecting Subdomain Tracking; Visits between subdomains may be misclassified as direct instead of referral. Implementing cross-domain tracking resolves this issue.
- Failing to Audit UTM Parameters Regularly: Inconsistent UTM tagging can fragment your data, making accurate attribution analysis difficult.
Advanced Techniques for Traffic Tracking
For businesses seeking greater precision in traffic attribution, a range of advanced tracking solutions can be implemented:
- Cross-Domain Tracking: Tracks user sessions seamlessly across multiple domains, preventing misclassification as direct traffic.
- Server-Side Tagging: Reduces the impact of ad blockers and ensures more reliable analytics data collection.
- Enhanced Attribution Models: Leverage Google Analytics 4’s machine learning-powered attribution to improve the accuracy of traffic source reporting.
How Direct Traffic Influences Conversion Rates
Direct traffic often reflects strong brand recognition, but it does not always translate into higher conversion rates. Research indicates that visitors from organic and referral channels generally exhibit greater engagement than direct traffic.
At the same time, repeat visitors arriving through direct traffic tend to demonstrate higher purchase intent. This makes it essential to segment these users and analyze their behavior separately for more actionable insights.
Using Technology to Optimize Direct Traffic Solutions
Advanced analytics platforms can help identify and correct misattributed traffic. By investing in robust analytics solutions, businesses gain deeper insights into user behavior and traffic sources, enabling more accurate and effective marketing strategies.
Understanding the Role of Direct Traffic in Marketing Strategy
Although frequently considered a catch-all category, direct traffic provides valuable insights into brand recognition and customer loyalty.
A high level of direct traffic can signal strong brand awareness and a dedicated audience. However, it is crucial to differentiate between authentic direct visits and misattributed sessions to accurately evaluate marketing effectiveness.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing direct traffic is critical for accurate data analysis and effective marketing strategies. By implementing comprehensive tracking, maintaining consistent protocols, and leveraging advanced analytics tools, businesses can achieve precise traffic attribution.
With this clarity, marketers can make informed decisions, optimize campaigns, and drive sustainable growth.
Analyzing your website traffic is just the first step. Transforming that data into actionable insights is where true growth occurs.